Responsible research & innovation (RRI) Project directory
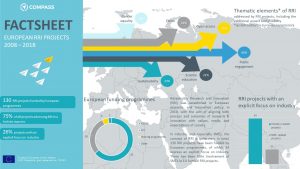
COMPASS has compiled an overview of RRI projects and initiatives carried out in Europe over the course of the past ten years. The COMPASS project directory below contains 130 publicly funded RRI projects in Europe. Our project directory aims to facilitate the search for RRI projects in Europe. You can download search instructions here.
For a quick look at the key figures check out our factsheet. For a detailed outline, have a look at the COMPASS policy paper, which maps out approaches, objectives and thematic priorities of publicly funded RRI projects at European level, and describes their spread across Europe via budget shares and numbers of participations.
You can find more information, results and project output on responsible innovation in the European Commission’s database CORDIS, as well as the RRI Toolkit!
Over the course of the project, it has become evident that rules, regulations and funding criteria could function as external incentives to implement responsible innovation in SMEs. The Vienna University of Economics and Business (WU), as coordinator of the COMPASS project, has therefore developed recommendations for EU research and innovation policy, with support of the COMPASS High Level Expert Advisory Board.
Responsible Innovation COMPASS
Evidence and Opportunities for Responsible Innovation in SMEs
Find out more